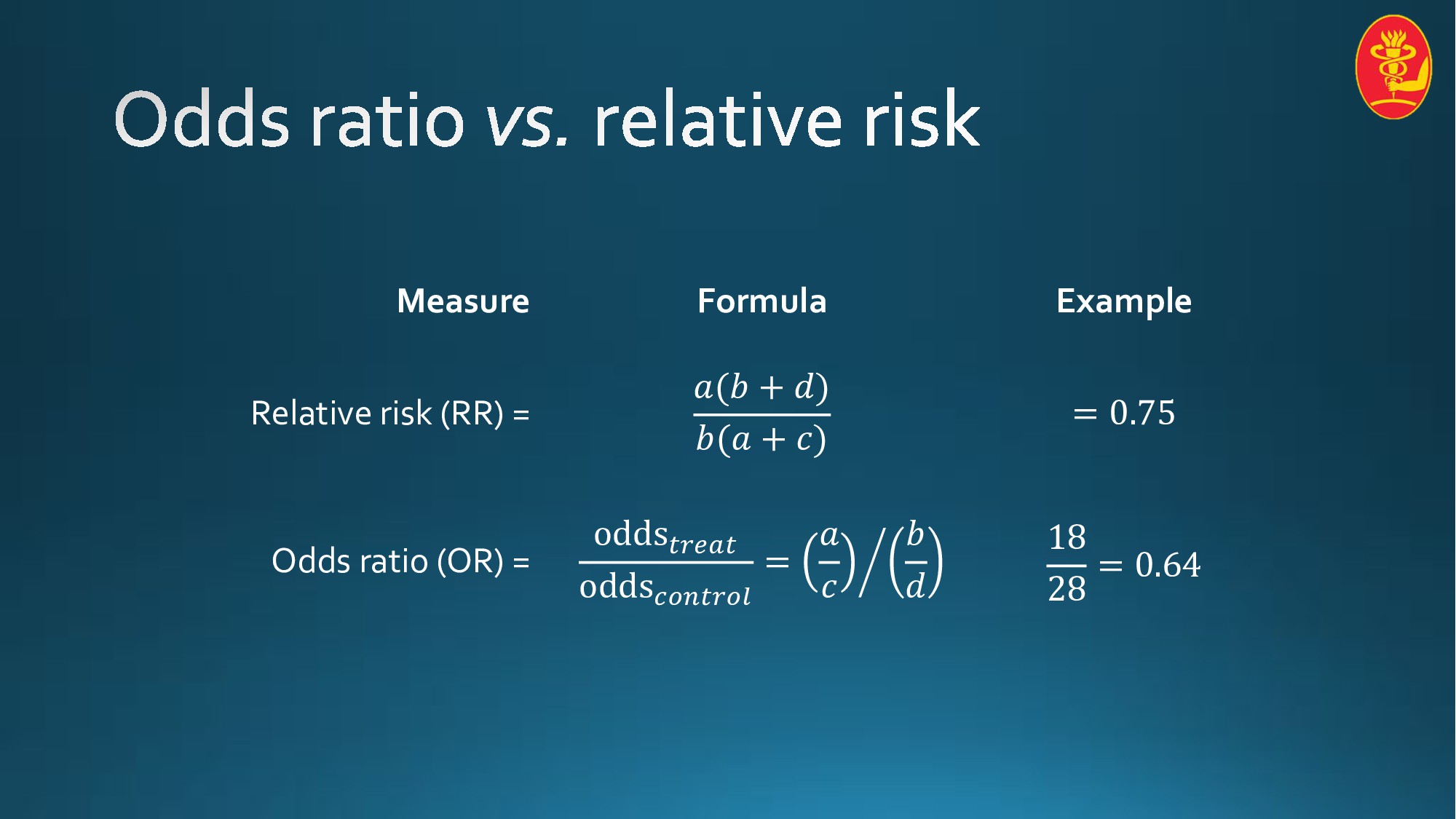
We can define the following terms The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated The odds ratio reflects the relative odds for the two groups—in this case, 656 ( ÷ ) This contrasts with the relative risk ratio, which is 524 (2381 ÷ 455) In some cases, the odds ratio and relative risk ratio are closer together, although the two ratios are calculated using different equations

What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
Odds ratio and relative risk examples
Odds ratio and relative risk examples-In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1Odds Ratio \u0026 Relative Risk Calculation \u0026 Definition, Probability \u0026 Odds Binary Logisitic Regression in SPSS with Two Dichotomous Predictor VariablesRelative Risk vs Odds ratio Confidence Interval Interpretation 95% Confidence Interval 90% 99% STATA Tutorials Binary Logistic Regression



Atrium Lib Uoguelph Ca Xmlui Bitstream Handle 1873 B Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Pdf Sequence 8
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents While the risk, as determined previously, of flipping a coin to be heads is 12 or 50%, the odds of flipping a coin to be heads is 11, as there is one desired outcome (event),Quote Relative Risk For casecontrol studies quote Odds Ratio Odds Ratio approximates Relative Risk for a rare disease in casecontrol studies For a crosssectional study one has a choice between Odds Ratio and Relative Risk 36
The relative risk is a measure of the strength of the effect of the drug treatment Another such measure is the odds ratio, which is the ratio of the odds in favor of a headache for the treatment group to the odds in favor of a headache for the control (or placebo) group found by evaluating psubt over 1 minus psubt all over psubc over 1Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterOdds ratio for the Titanic example is OR= 376 037 = 1016 This is very different from the relative risk calculated on the same data and may come as a surprise to some readers who are accustomed of thinking of odds ratio as of relative risk (Greenland, 1987)
So if the probability of having liver disease among habitual alcoholic beverage drinkers is % and among nonalcoholic beverage drinkers is 2% the OR will be = %/ (1%) / 2%/ (21%/)=1225 and the RR of having liver disease when drinking alcoholic beverages will be = %/2%=10The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Odds Ratio = Odds / OddsThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions



Risk A Statistician S Viewpoint Speaker Deck




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
The odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome ORAdmissions Example – Calculating the Odds Ratio Example admissions to a graduate program Assume 70% of the males and 30% of the females are admitted in a given year Let P equal the probability a male is admitted Let Q equal the probability a female is admitted Odds males are admitted odds(M) = P/(1P) = 7/3 = 233 Technically, relative risk should not be used to express results in casecontrol studies because the disease prevalence is not known and the apparent relative risk is dependent on the number of controls chosen 4 However, the odds ratio is a reasonable approximation of the relative risk when the outcome is relatively rare (eg, when less than 1%




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Fisioterapeuta Luis Miguel Brazao Gouveia Guide To Biostatistics
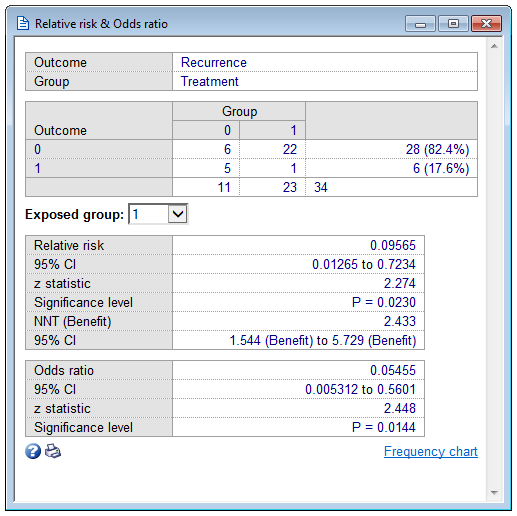
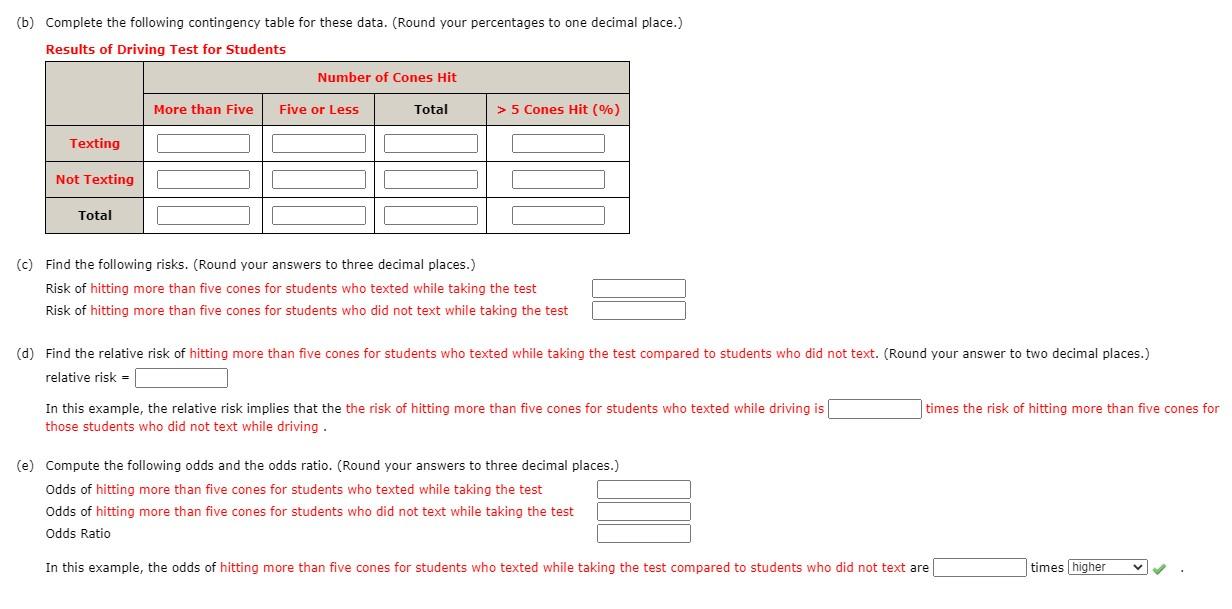
EXAMPLES Calculating Risk Ratios Example A In an outbreak of tuberculosis among prison inmates in South Carolina in 1999, 28 of 157 inmates residing on the East wing of the dormitory developed tuberculosis, compared with 4 of 137 inmates residing on the West wing These data are summarized in the twobytwo table so called because it has two rows for the exposure and twoBoth the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the oddsA value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical



Ctspedia Ctspedia Riskratio



Relative Risk Odds Ratio
Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently ( a relative risk ratio is one probability divided by another;Relative Risk Relative risk is a ratio of the risks of two groups In the example described above, it would be the risk of heart attack for a person in their current condition compared to the risk of heart attack if that person were in the normal ranges However, to truly interpret the severity of a relative risk we have to know the baseline risk




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThis video will show you how to calculate and interpret odds ratios and risk ratios with an exampleFor more assistance with statistics, consider this bookM



Contingency Table And Risk Relative Risk Odds Chegg Com



Www Pitt Edu Bertsch Risk Pdf
Rate ratios are closely related to risk ratios, but they are computed as the ratio of the incidence rate in an exposed group divided by the incidence rate in an unexposed (or less exposed) comparison group Consider an example from The Nurses' Health Study This prospective cohort study was used to investigate the effects of hormone replacement therapy Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;Odds Ratio, Likelihood Ratio, Relative Risk Pvalue OR LR RR Lactose Intolerance rs495 8e4 55 145 15 Eye Color rs 1e7 Large 155 16 Bitter Taste rs 7e7 45 195 28 Earwax rs 1e14 18 402 34




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Atrium Lib Uoguelph Ca Xmlui Bitstream Handle 1873 B Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Pdf Sequence 8
For example, the odds of a tiger being diseased, divided by the odds of a bear being diseased This diagram demonstrates with some simulated data the core concepts Tigers have a 1/4 (025) probability of being diseased, which is "1 to 3" odds of being diseasedTo calculate the odds ratio, we use one of the following formulas (both give the same outcome) Example 2 We compare smokers and nonsmokers with regard to the presence of ischemic heart disease The following table shows the results Example 2 We can now calculate the odds ratio (10/40) / (5/45) = 225Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)




Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Ppt Pobierz
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio is from 10, the more likely it is that the relationship between the exposure and the disease is causal For example, an odds ratio of 12 is above 10, but is not a strong association An odds ratio of 10 suggests a stronger associationRelative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878




Present Example Of An Dolds Ratio Compared To A Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube
Figure 1 shows the underestimation of the relative risk by the odds ratio in studies that report odds ratios of less than one (typically studies of benefit from treatment or exposure) Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with aIt is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865 What does a risk ratio of 075 mean?In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio Similarities




Assessment Of Multiplicative Interaction Using Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram



The Difference Between Probability And Odds
In prospective trials, it is simply a different way of expressing this association than relative risk The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Openepi 2 X 2 Table Statistics
an odds ratio is one set of odds divided by another;Odds = Probability / (1probability) Odds ratio (OR) = ratio of odds of event occurring in exposed vs unexposed group Odds ratio are used to estimate how strongly a variable is associated with the outcome of interest; Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out to




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




3 Data For Example 7 3 To Illustrate The Need For The Disease To Be Download Table
For example the probability of a tiger being diseased, divided by the probability of a bear being diseased A lot of confusion would be saved (in my view) if we could call these "probability ratios" instead, but the term "relative risk ratio" seems to be here to stayThe odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol Unless I'm mistaken, the equation explained above does not properly describe Odds Ratio, it describes Relative Risk Odds Ratio is the odds that the diseased group was exposed, divided by odds that the nondiseased group was exposed (a/c)/(b/d) in the classic table (see comment 91 for a stark example) The p value is the risk of




Relative Risk Analysis And Odds Ratio Analysis




상대위험도 Relative Risk Vs 오즈비 Odds Ratio
The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal An example of what I am talking about is the choice between risk ratio and odds ratio Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjectsThe relative risk The relative risk can be calculated as ratio between two incidence proportions (risk ratio, see Example 1) or two incidence rates (incidence rate ratio, see Example 2) Example 1 In the randomized prospective, Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) study,1 the effect of ramipril on the risk of cardiovascular (CV) events
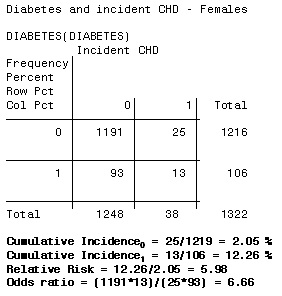



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507




Exploratory Data Analysis With Two Qualitative Variables Not
Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Please Answer All Questions Parts Step By Step Chegg Com




How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
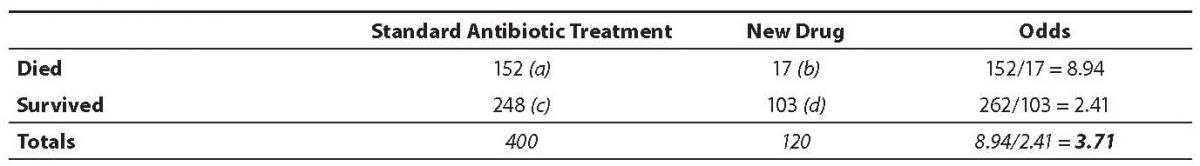



The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Youtube
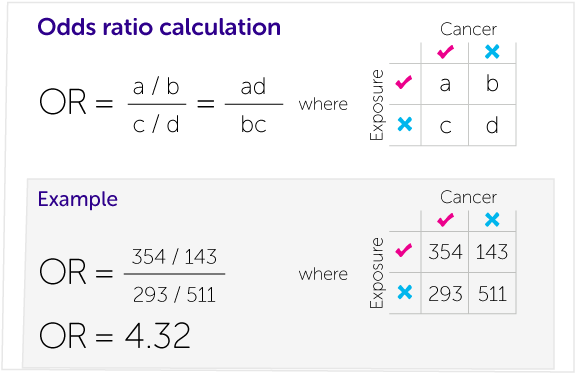



Our Calculations Explained Cancer Research Uk




Evidence Of Safety Pooled Relative Risk Rr Or Odds Ratio Or And Download Table




Evaluating Results The Best Evidence So Far Weve



Arxiv Org Pdf 1510




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
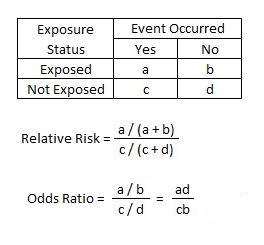



Relative Risk Article




Slides Show



1




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



Calculating Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Rate Ratio Youtube




Relative And Atribute Risk
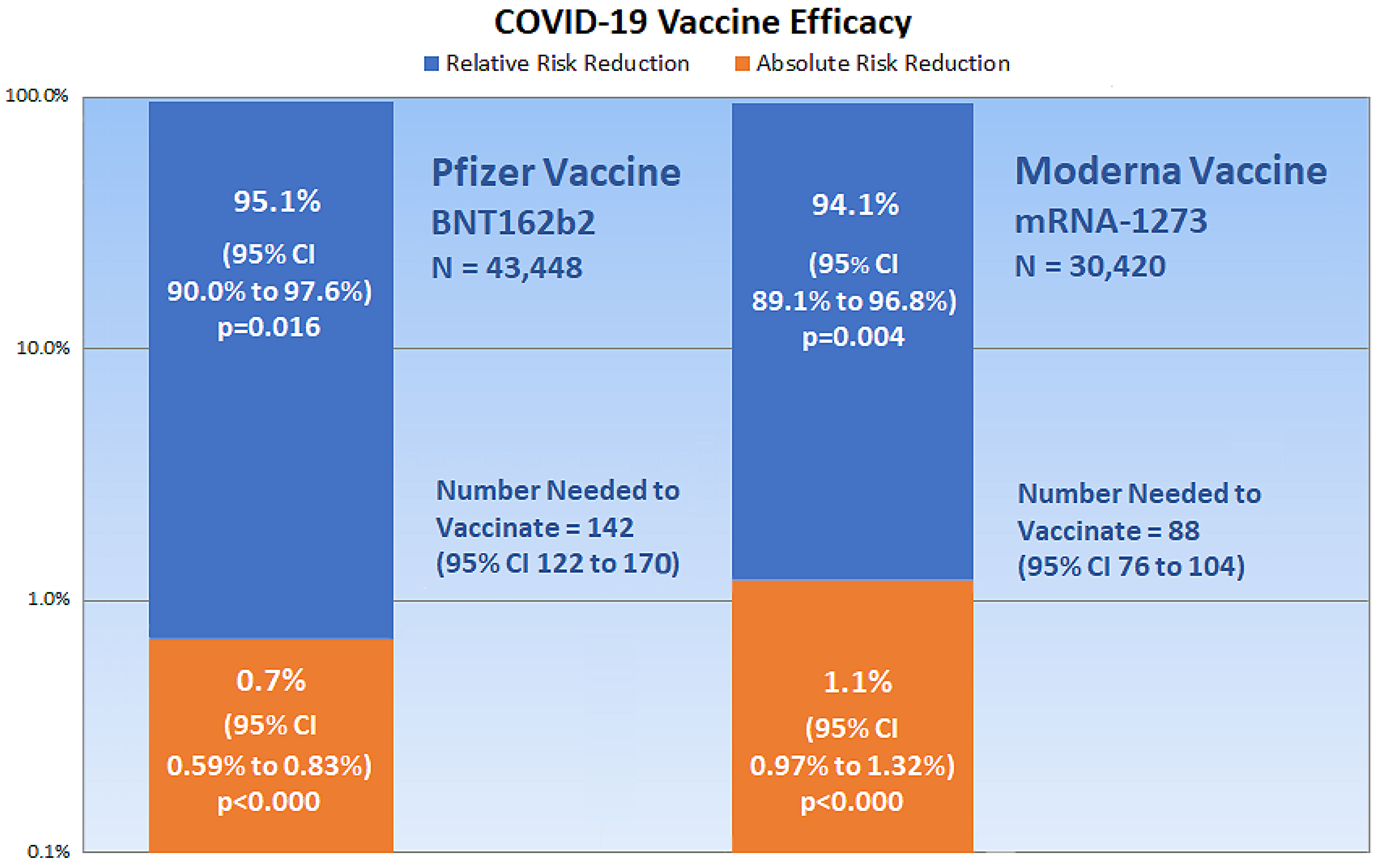



Medicina Free Full Text Outcome Reporting Bias In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Clinical Trials Html




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




12 Biostats Ideas Regression Analysis Linear Regression Chi Square



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Odds Ratio Article



Relative Risk Wikipedia




James Deardorff Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Odds Ratio Measures Solely The Effect Magnitude And Has No Relationship



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
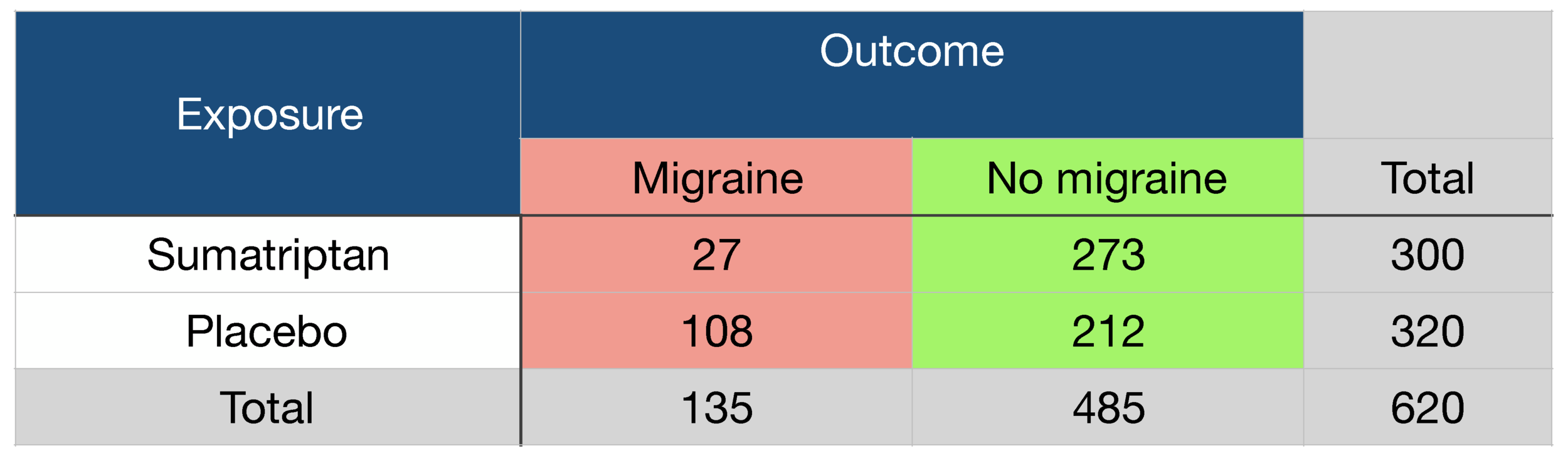



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj



1
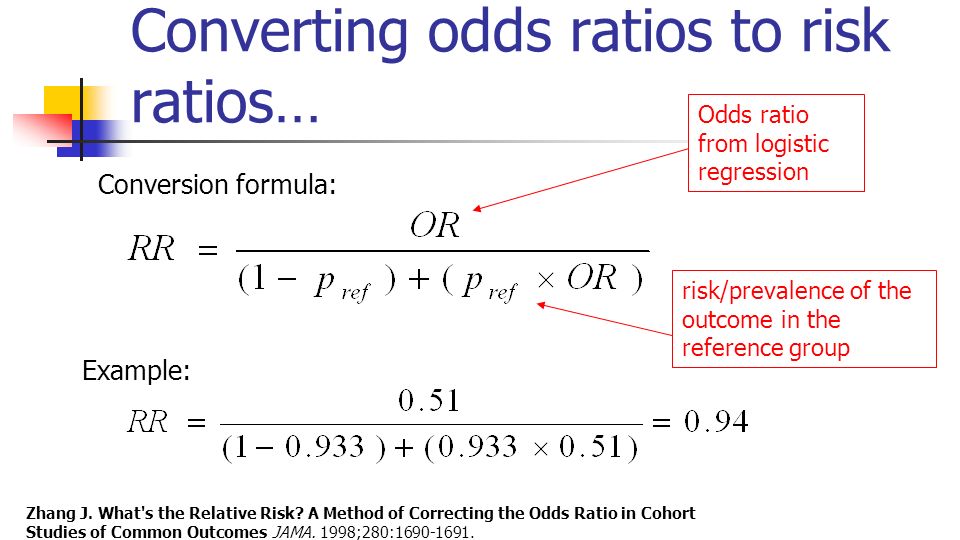



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Table 1 From Identifying The Odds Ratio Estimated By A Two Stage Instrumental Variable Analysis With A Logistic Regression Model Semantic Scholar



Summarising Binary Data Health Knowledge




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj
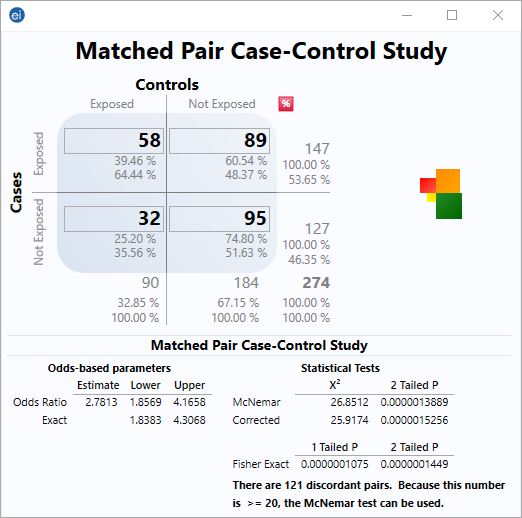



Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf




Relative Risks Odds Ratios The Odds Ratio Two Binomials Coursera




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Lecture 5 Agenda Basic Contingency Table Analysis Rx




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To
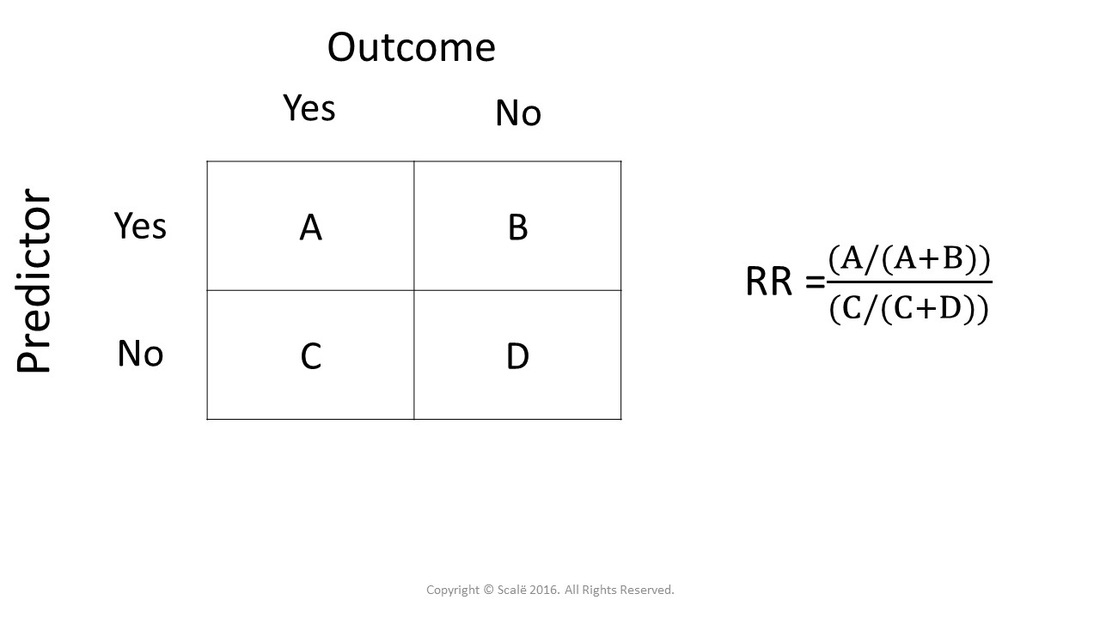



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data




Relative Risks Odds Ratios Relative Measures Two Binomials Coursera




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
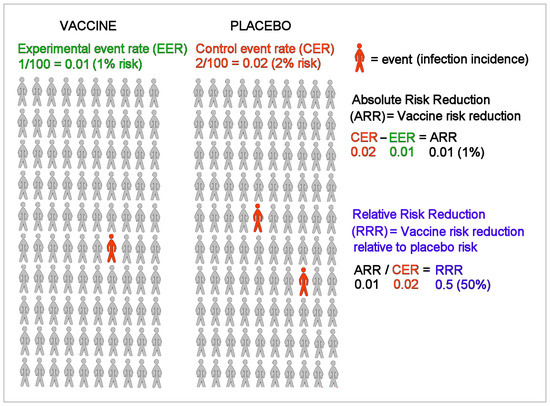



Medicina Free Full Text Outcome Reporting Bias In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Clinical Trials Html



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



Www Jstor Org Stable
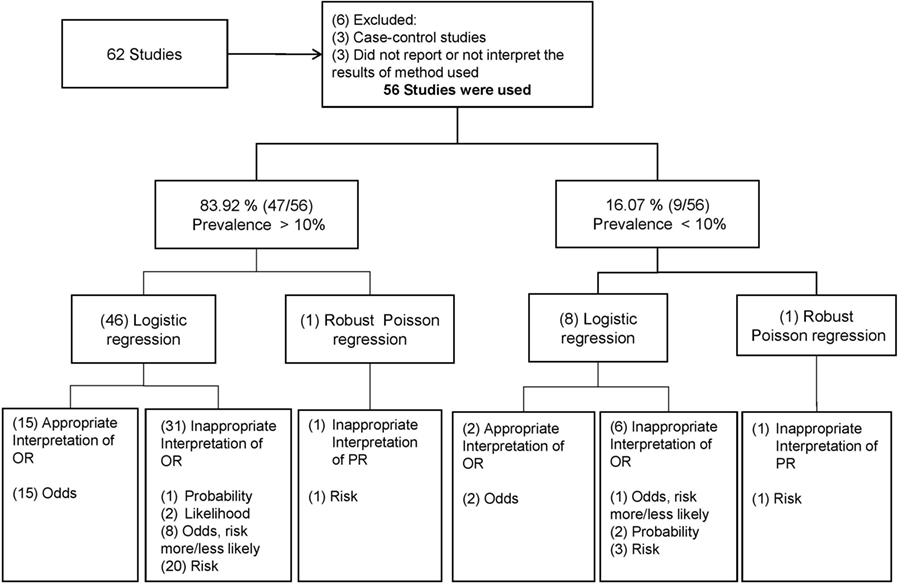



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge




Measures Of Association Ppt Video Online Download




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



2




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Understanding Absolute And Relative Risk In Medical Risk Analysis And Putting This In Context




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Relative And Atribute Risk




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Q Tbn And9gcs7g3 Oy3gxo7fbk7uvklwexnnbqcmd7m5bqd Ghq64ww9hd4dh Usqp Cau




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney On Prezi Next




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean


